Ancaster Foot Fixer and Orthotics Clinic
Athletes Foot
Athletes Foot
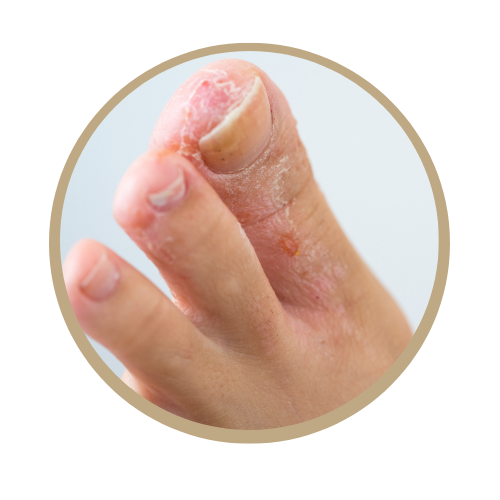
Athlete's foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet, particularly between the toes. It is a contagious condition caused by various types of fungi, most commonly the group known as dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making the feet, especially the spaces between the toes, an ideal breeding ground.
Causes of Athlete's Foot:
-
Fungal Infection: The primary cause of athlete's foot is exposure to fungi, typically found in warm and damp environments like locker rooms, public showers, swimming pools, and communal areas. The fungi responsible for athlete's foot can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person or by touching surfaces contaminated with the fungi.
-
Moisture and Sweating: Prolonged moisture on the feet, often caused by sweating or wearing tight, closed-toe shoes, creates an environment conducive to fungal growth. This is why athlete's foot is more common among athletes, as the name suggests, due to their frequent use of sports shoes and exposure to communal areas.
-
Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV, may be more susceptible to fungal infections, including athlete's foot.
-
Poor Foot Hygiene: Inadequate foot hygiene, including not drying the feet thoroughly after bathing or exercise, can contribute to the development of athlete's foot.
Common Symptoms of Athlete's Foot:
- Itching and burning sensations, especially between the toes.
- Redness and inflammation.
- Peeling, cracking, or flaking skin, often in a circular pattern.
- Blisters or ulcers in severe cases.